方法编码 概念
To assist the runtime system, the compiler encodes the return and argument types for each method in a character string and associates the string with the method selector.
为了辅助运行时系统,编译器对字符串中每个方法的返回和参数类型进行编码,并将字符串与方法选择器相关联
OC类型编码表
字符
含义
c
A char
i
An int
s
A short
l
A long l is treated as a 32-bit quantity on 64-bit programs.
q
A long long
C
An unsigned char
I
An unsigned int
S
An unsigned short
L
An unsigned long
Q
An unsigned long long
f
A float
d
A double
B
A C++ bool or a C99 _Bool
v
A void
*
A character string (char *)
@
An object (whether statically typed or typed id)
#
A class object (Class)
:
A method selector (SEL)
[array type]
An array
{name=type…}
A structure
(name=type…)
A union
bnum
A bit field of num bits
^type
A pointer to type
?
An unknown type (among other things, this code is used for function pointers
详情参考:Type Encoding
在上一节使用method_getTypeEncoding 打印出方法列表时
1 2 3 4 5 ... 'NSString' |'initWithFormat:locale:arguments:' of encoding '@40@0:8@16@24[1{__va_list_tag=II^v^v}]32' 'NSString' |'initWithCoder:' of encoding '@24@0:8@16' 'NSString' |'initWithString:' of encoding '@24@0:8@16' ...
1 2 * Returns a string describing a method's parameter and return types.
方法是如何编码的
为什么NSString 的initWithString 的编码是*@24@0:8@16*
Google了一下
Apple Mail List: method_getTypeEncoding returns strange string
里面主要说了两个事情
为什么有这么多的@:之类的
因为OC方法默认带了self 和*_cmd*这两个参数,所以这也是为什么能直接在方法中用这两个”关键字”的原因,所以配合上面的编码表 @(返回值)24@(self)0:(_cmd)8@(第一个参数NSString)
关于数字代表什么意思? 帖子上说法不太统一, 有说是栈偏移量(Stack offset)的,有说和(arm,ppc,x86_64)平台相关。
尝试查了源码,调试了半天,不太成功,并不是明显的有一个生成规则。经过观察,发现*@0:8是每个方法都是一样的(NSString 类),结合上面的含义 0 用来描述 self*,8用来描述*_cmd*,想到self 指向该类地址基地址,偏移量正好为0,因此揣测数字的意思应该是相对于类的基地址的偏移量
数据类型 Ivar Ivar 用于表示类的实例变量的类型
定义如下
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 struct objc_ivar { char *ivar_name OBJC2_UNAVAILABLE; char *ivar_type OBJC2_UNAVAILABLE; int ivar_offset OBJC2_UNAVAILABLE; #ifdef __LP64__ int space OBJC2_UNAVAILABLE; #endif }
测试代码
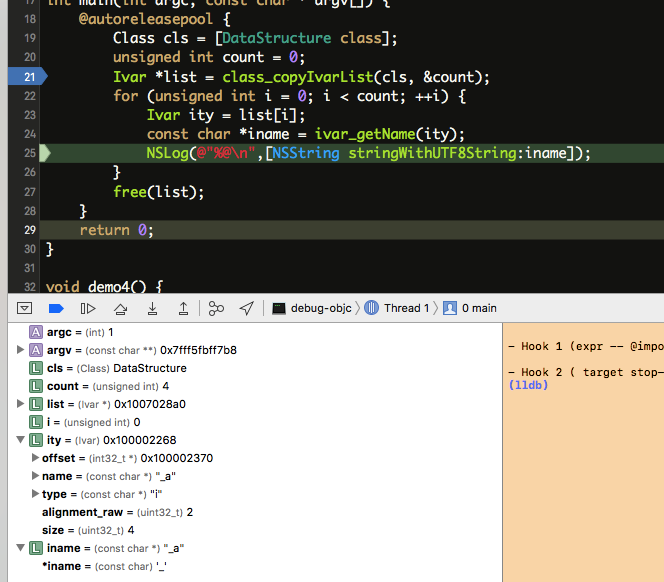
定义了一个DataStructure 类
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 @interface DataStructure : NSObject int _a; long _b; char _c; NSArray *_d; } int main(int argc, const char * argv[]) { @autoreleasepool { Class cls = [DataStructure class ]; unsigned int count = 0 ; Ivar *list = class_copyIvarList(cls, &count); for (unsigned int i = 0 ; i < count; ++i) { Ivar ity = list[i]; const char *iname = ivar_getName(ity); NSLog (@"%@\n" ,[NSString stringWithUTF8String:iname]); } free(list); } return 0 ; }
type : i 整数name : _a offset : 0x1007028a0
objc_property_t objc_property_t 用于表示类的属性的类型
1 2 3 typedef struct objc_property *objc_property_t;
1 2 typedef struct property_t *objc_property_t;
都是指向objc_property 结构体的指针
objc_property 结构体的定义
1 2 3 4 5 struct property_t { const char *name; const char *attributes; };
里面有个指针attributes 指向objc_property_attribute_t 结构体的数组
1 2 3 4 5 6 typedef struct { const char *name; const char *value; } objc_property_attribute_t;
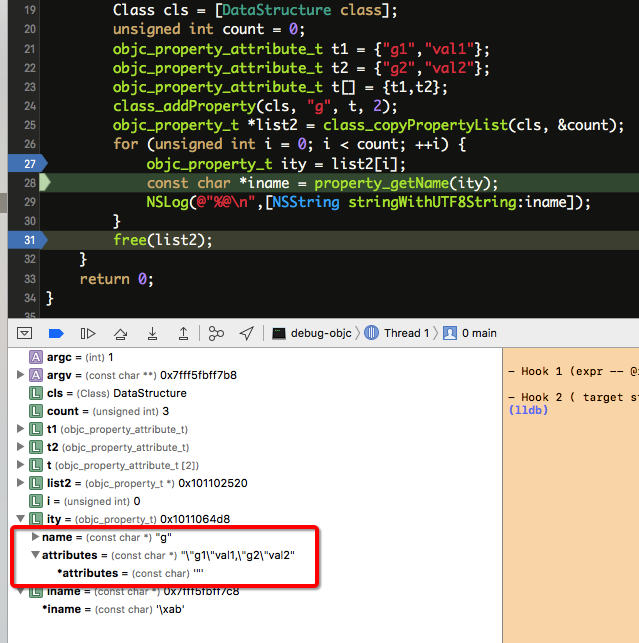
测试代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 int main(int argc, const char * argv[]) { @autoreleasepool { Class cls = [DataStructure class ]; unsigned int count = 0 ; objc_property_attribute_t t1 = {"g1" ,"val1" }; objc_property_attribute_t t2 = {"g2" ,"val2" }; objc_property_attribute_t t[] = {t1,t2}; class_addProperty(cls, "g" , t, 2 ); objc_property_t *list2 = class_copyPropertyList(cls, &count); for (unsigned int i = 0 ; i < count; ++i) { objc_property_t ity = list2[i]; const char *iname = property_getName(ity); NSLog (@"%@\n" ,[NSString stringWithUTF8String:iname]); } free(list2); } return 0 ; }
objc_property_t 中的attributes 指针确实指向了通过class_addProperty 函数添加到类中,类型为objc_property_attribute_t 结构体的数组
关联对象(Associated Object) OC 中要想给原有的类添加方法,要么是动态添加,另一种就是分类(Category),但是分类时,不能添加实例变量,编译器不允许,可以通过关联对象进行绑定,同时还可以指定管理策略,像使用*@property*一样方便。
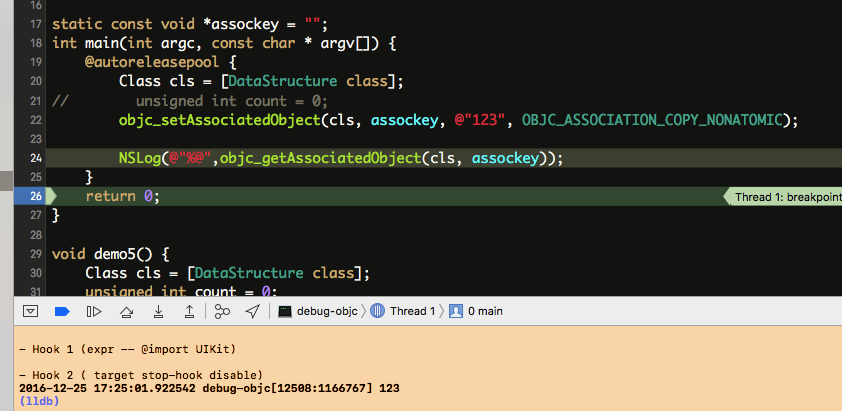
测试代码:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 static const void *assockey = "" ;int main(int argc, const char * argv[]) { @autoreleasepool { Class cls = [DataStructure class ]; objc_setAssociatedObject(cls, assockey, @"123" , OBJC_ASSOCIATION_COPY_NONATOMIC); NSLog (@"%@" ,objc_getAssociatedObject(cls, assockey)); } return 0 ; }
跟进去得到
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 void _object_set_associative_reference(id object, void *key, id value, uintptr_t policy) { ObjcAssociation old_association(0 , nil ); id new_value = value ? acquireValue(value, policy) : nil ; { AssociationsManager manager; AssociationsHashMap &associations(manager.associations()); disguised_ptr_t disguised_object = DISGUISE(object); if (new_value) { AssociationsHashMap::iterator i = associations.find(disguised_object); if (i != associations.end()) { ObjectAssociationMap *refs = i->second; ObjectAssociationMap::iterator j = refs->find(key); if (j != refs->end()) { old_association = j->second; j->second = ObjcAssociation(policy, new_value); } else { (*refs)[key] = ObjcAssociation(policy, new_value); } } else { ObjectAssociationMap *refs = new ObjectAssociationMap; associations[disguised_object] = refs; (*refs)[key] = ObjcAssociation(policy, new_value); object->setHasAssociatedObjects(); } } else { AssociationsHashMap::iterator i = associations.find(disguised_object); if (i != associations.end()) { ObjectAssociationMap *refs = i->second; ObjectAssociationMap::iterator j = refs->find(key); if (j != refs->end()) { old_association = j->second; refs->erase(j); } } } } if (old_association.hasValue()) ReleaseValue()(old_association); }
大致原理是有个AssociationsHashMap 将key 和value 进行关联,根据注释,可以得出,如果key 相同时,retain 新值release 旧值
方法的执行 前面说了,OC是一门动态的面向对象编程语言,它脱胎于Smalltalk Wiki
Smalltalk 中的消息机制被OC采用并传承下来
Messages
而它与*C++*这种函数调用(function calling )区别在于。运行时所应执行的代码由运行环境来决定;而使用函数调用的语言,则由编译器决定。
先了解一些概念
SEL SEL 与Method 有关,看下Method
Method 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 typedef struct objc_method *Method;struct objc_method { SEL method_name OBJC2_UNAVAILABLE; char *method_types OBJC2_UNAVAILABLE; IMP method_imp OBJC2_UNAVAILABLE; } OBJC2_UNAVAILABLE;
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 typedef struct method_t *Method;struct method_t { SEL name; const char *types; IMP imp; struct SortBySELAddress : public std::binary_function<const method_t&, const method_t&, bool > { bool operator() (const method_t& lhs, const method_t& rhs) { return lhs.name < rhs.name; } }; };
一个Method 包含
1 2 3 SEL name*: const char * types: IMP imp:
1 2 3 typedef struct objc_selector *SEL;
代码验证
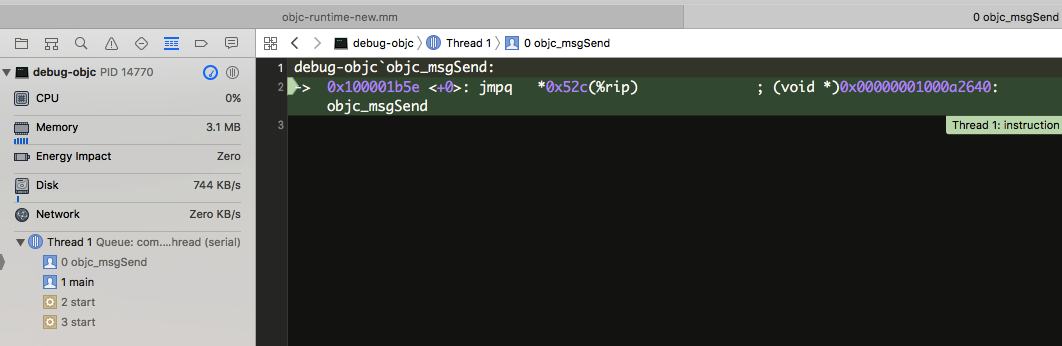
当向一个OC对象执行方法(发送消息)时,方法在底层会转换成调用*objc_msgSend( )*函数
该函数的原型为void objc_msgSend(id self, SEL cmd,…)
该函数通过SEL 在self 对象的列表中找指定的方法
测试代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 int main(int argc, const char * argv[]) { @autoreleasepool { NSObject *cls= [[NSObject alloc] init]; [cls debugDescription]; } return 0 ; }
按指令级别调试 ⌃ + F7 功能键开启情况下,要加上fn,
从调用堆栈看确实调用了objc_msgSend ,再继续跟进,会进到objc-msg-x86_64.s (因为是macOS 的源代码)
当然还有其他的一些情况,会交由Objective-C 运行环境中的另外一些函数来处理
objc_msgSend_stret : 发送消息要返回结构体,交由此函数处理objc_msgSend_fpret :发送消息返回的是浮点数,交由此函数处理objc_msgSendSuper : 给父类发送消息,交由此函数处理
现在我们已经知道哪个对象(self )要接收消息(SEL ),但是消息具体执行什么?Method 结构体已经告诉了到,就是那个IMP ,如果我们要知道那个IMP ,一种方法就是用一个表去关联方法名(SEL )和方法实现(IMP ),这样在objc_msgSend 中就可以根据方法名(SEL )去找到方法实现(IMP )
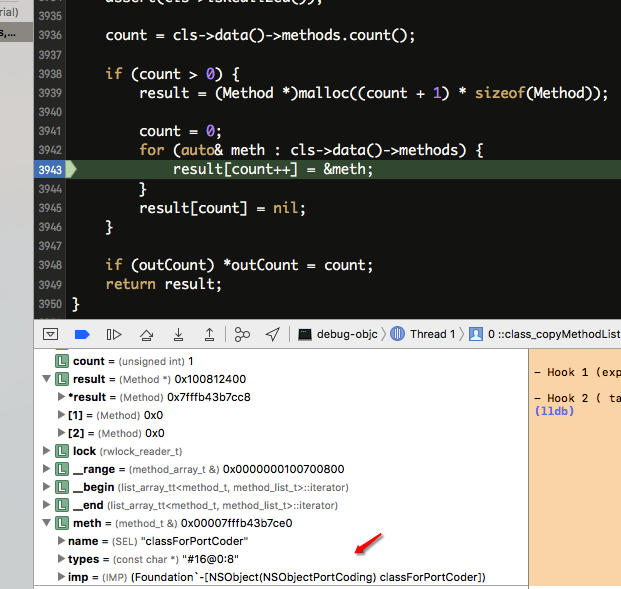
第二部分,在探究类的结构时,曾使用class_copyMethodList 得到方法列表,打断点,进入objc-runtime-new.mm
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 Method * class_copyMethodList(Class cls, unsigned int *outCount) { unsigned int count = 0 ; Method *result = nil ; if (!cls) { if (outCount) *outCount = 0 ; return nil ; } rwlock_reader_t lock(runtimeLock); assert(cls->isRealized()); count = cls->data()->methods.count(); if (count > 0 ) { result = (Method *)malloc((count + 1 ) * sizeof (Method)); count = 0 ; for (auto& meth : cls->data()->methods) { result[count++] = &meth; } result[count] = nil ; } if (outCount) *outCount = count; return result; }
其中有一句 cls->data()->methods.count()
看看cls->data()->methods
直接调试里面的代码
方法转发 在第二部分的方法调用中,知道了查找方法的顺序,因为OC的动态性,在编译期间向类发送了其无法解读的消息,并不会报错,但是当运行时,发现接收者确实无法响应消息时,就会报unrecognized selector sent to instance 0x87 ** Terminating app due to uncaught exception NSInvalidArgumentException…*,但是在此之前,OC 还会启动“消息转发”(message forwarding )机制,让程序员有机会告诉对象如何处理未知消息。
动态方法解析 接收者是对象
1 + (BOOL )resolveInstanceMethod:(SEL)selector
接收者是类
1 + (BOOL )resolveClassMethod:(SEL)selector
selector 参数为未识别的方法
备援接收者 1 - (id )forwardingTargetForSelector:(SEL)selector
selector 参数为未识别的方法id 返回类型代表能识别selector 方法的对象,如果没有,返回nil
测试代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 int main(int argc, const char * argv[]) { @autoreleasepool { DataStructure *d = [[DataStructure alloc] init]; [d performSelector:@selector (haha)]; } return 0 ; } - (id )forwardingTargetForSelector:(SEL)aSelector { return [[NewTarget alloc] init]; } @interface NewTarget : NSObject - (void )haha; @end @implementation NewTarget - (void )haha { NSLog (@"haha" ); } @end
将发送给DataStructure 类的haha 消息让NewTarget 类去响应
该方法配合组合 的形式,可以模拟多继承的效果
完整的消息转发 启动完整的消息转发机制,创建NSInvocation 对象,封装未响应对象的SEL ,target 及参数,调用
1 - (void )forwardInvocation:(NSInvocation *)invocation
使用该方法可以修改消息内容,追加参数,更改SEL 等
方法交换(Method Swizzling) 从上面也可以知道,OC中可以在运行时,动态添加方法,改变接收对象,消息改变与转发等。因为Method 方法有SEL 与IMP ,可以通过修改SEL 指向的IMP ,达到方法交换的效果。
代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 + (void )hookMethod:(Class)cls OriginSelector:(SEL)originalSelector SwizzledSelector:(SEL)swizzledSelector { Method originalMethod = class_getInstanceMethod(cls, originalSelector); Method swizzledMethod = class_getInstanceMethod(cls, swizzledSelector); BOOL didAddMethod = class_addMethod(cls, originalSelector, method_getImplementation(swizzledMethod), method_getTypeEncoding(swizzledMethod)); if (didAddMethod) { class_replaceMethod(cls, swizzledSelector, method_getImplementation(originalMethod), method_getTypeEncoding(originalMethod)); } else { method_exchangeImplementations(originalMethod, swizzledMethod); } }
参考